The goal of the corporation is to maximize money for shareholders. If the corporation is making a profit and management gets rewarded for profits, shouldn’t their interests be aligned? NO! Many times management is more concerned with short-term profits that maximize how good they look, where as shareholders want to maximize profits period, not at the expense of later periods. There’s also a problem of shareholders having high demands on a quarterly basis (when financial statements are released) that stress managements’ plans for the future.
Corporations have much more complex structures than other forms of organization and therefore problems come along the way.
One key difference between corporations and other forms of organization is separation of control and ownership. The agency problem, also known as the “principal-agent problem”, is a conflict of interest when someone (the principal) hires another (the agent) to act in his or her best interests. The problem is that the agent is supposed to make decisions to best serve the principal’s best interests while the agent’s own best interests may be different from the principal’s best interests. In a corporation, the management is the agent and the stockholders are the principal. For example: a firm is considering a new investment which is expected to positively impact the stock price, but it is considered to be relatively risky. According to the shareholders’ best interest, the firm should take the investment as the stock price will rise, while the management may prefer not because it is possible that the investment will go bad given the high risk and they will lose their job because of the bad performance. If the management doesn’t make the investment, the shareholders lose the opportunity of gaining more potential earnings – it is called agency cost.
To solve the agency problem, there are generally two solutions:
- Control of the firm. To monitor the management and ultimately control the firm, the shareholders elect board of directors who hires and fires management. The managers are under the pressure of the board to try to maximize the wealth of the shareholders, or else they will be replaced.
- Managerial compensation. It is impossible for the board to monitor the management perfectly. An alternative to monitoring is to motivate the managers to act in shareholders’ best interests through compensation, including performance-based bonuses, stock options, and promotion.
Sometimes the agency problem situation can be very complex. For example, management’s performance is measured by the company’s performance in both the short term and the long term, therefore the decision they made are based on a long-term goal. However many shareholders, who don’t intend to hold the stock for a long time, are more interested in immediate return therefore they prefer a dividend instead of reinvesting the money to achieve a long-term development and growth which is not the perfect way to operate the business. Another example is the board of directors may have a different opinion from the shareholders and the management. Conflicts among three entities can be very difficult to resolve.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Business Organization Types
It is important to understand the different types of business organizations types such as a sole proprietorship, partnership, and corporation. A business’s organizational structure influences issues, legal issues, financial concerns, and personal concerns.
A Sole Proprietorship is a business with one owner who operates the business on his or her own or employ employees. It is the simplest and the most numerous form of business organization in the United States, however it is dangerous as the sole proprietor has total and unlimited liability. Self contractor is one example of a sole proprietorship.
Advantages of a sole proprietorship
- Simplest and least expensive form of business to establish and to dissolve.
- The owner is making all the decisions and controlling the whole operations.
- All profit flows directly to the owner.
- It is subject to fewer regulations.
- It has tax advantage: any income is declared as the owner’s personal income tax return, therefore there are no corporate income taxes.
Disadvantages of a sole proprietorship
- The owner is responsible for all the obligations of the business.
- It is difficult to raise capital: it can only use the owner’s personal saving and consumer loans.
A Partnership is a business with two or more individuals owns and manages the business. Partners share the unlimited liabilities of the business and operate the business together. There are three classification of partnerships: general partnership (partner divide responsibility, liability and profit or loss according to their agreement), limited partnership (in additional at least one general partner, there are one or more limited partner who have limited liability to the extent of their investment), and limited liability partnership (all of the partners have limited liability of the business debts; it has no general partners).
Advantages of a partnership
- It is relatively easy to form but considerable amount of time should be invested in developing the partnership agreement.
- It is easier to raise capital compared to a sole proprietorship as there are more than one investor.
- Any income is declared as the partners’ personal income tax returns, therefore there are no corporate income taxes.
- Employees may be motivated and attracted to the business by the inventive to become a partner
Disadvantages of a partnership
- Partners are jointly responsible for all the obligations of the business.
- Partners must make decision together therefore disputes or conflicts may occur. It may eventually lead to dissolving the partnership.
A corporation is a limited liability entity doing business owned by multiple shareholders and is overseen by a board of directors elected by the shareholders. It is distinct from its owners and can borrow money, enter into contracts, pay taxes and be sued. The shareholders gain from the profit through dividend or appreciation of the stocks but are not responsible for the company’s debts.
Advantages of a corporation
- It can raise additional funds through the sale of stock.
- Shareholders can easily transfer the ownership by selling their stock.
- Individual owner’ liability is limited to the value of stock they are holding in the corporation.
Disadvantages of a corporation
- It is restricted by more regulations, more closely monitored by governmental agencies and are more costly to incorporate than other forms of the organizations.
- Profit of the business is taxed by the corporate tax rate. Dividends paid to shareholders are not deductible from corporate income, so this part of income is taxed twice as the shareholders must declare dividends as their personal income and pay personal income taxes too.
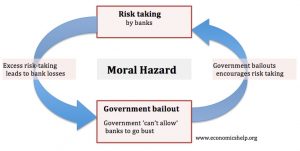
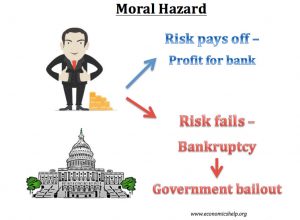
What is Moral Hazard?
Moral hazard is the act of engaging in activity that serves the interest of the managers over the owners of the corporation. It is the result of the principal/agent problem, where the person who makes the decisions does not bear the consequences of that decision. Moral hazard encompasses four areas: 1. Insufficient Effort, 2. Investment in Extravgant Projects, 3. Entrenchment Strategies, 4. Self- Dealing.
1. Insufficient Effort- When the manager cares more about his time on the golf course and entertaining celebrities more than the inner workings of the company, the company is weaker. Manager’s may avoid unpleasant tasks, such as firing incompetent employees or monitoring key operations. Insufficient effort may be the result of incompetence or of significant extra-curricular activities.
2. Investments in Extravagant Projects- Manager’s engage in pet projects to build an “empire” or because of a certain personal interest at the expense of shareholder’s. Empirical evidence has proven that these extravagant projects do not result in a positive shareholder benefit. This is typically a problem when the company has excess cash to spend.
3. Entrenchment Strategies- An entrenchment strategy is an effort by a manager to make himself irreplaceable. A manager may pursue a strategy that may not be in the best interest of shareholders, but would make the manager look good because he runs it efficiently. In addition, a manger may attempt to resist a takeover even though it may benefit the shareholder.
4. Self-Dealing- This is when the manager uses the company credit card as a personal benefit. Examples include using company assets for personal use, using company funds for a favored political candidate, or lavish office decoration expenses.